
For example: cd /Volumes/Elements/ to access an external drive called “Elements.” Use the cd command to change directories. In this example, rm is the delete command, the -i flag instructs the process to ask for user confirmation, and would be replaced with the file or folder’s location on the drive. Flags are case-sensitive. The flag always appears after the command. For example, the -R flag applies a command recursively so that it applies to a directory, all files and folders within that particular directory, all files and folders inside those folders, and so on. Most commands can be appended with a flag in the form of a hyphen and a letter to access different functions.
Command prompt commands cd example how to#
When we’re done, you might want to learn how to lock your Mac from the Terminal, or even how to shut it down with a simple command. These will be familiar to you if you’ve ever used the Linux command line, too. We’ll cover some of the most basic Mac terminal commands here. Cut, copy, and paste all work as expected, and you can drag any file or folder into the Terminal window to immediately skip to that directory.

You can open multiple tabs with Command+T or a new Terminal window with Command+N. Many of the shortcuts that you use in other apps will work here.
Launch Terminal by finding it in the Utilities folder or by searching for it using Spotlight, and then familiarize yourself with the interface. This is how you execute commands on your Mac using the command line. An additional way to change the CWD to another drive without the usage of the cd command is to execute the drive letter followed by a colon.Your Mac comes with an app called Terminal under Applications > Utilities.
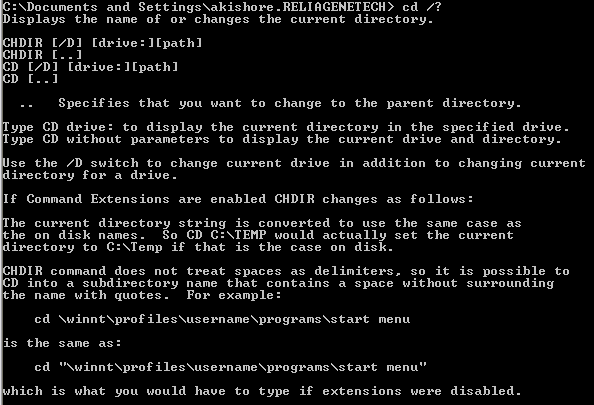
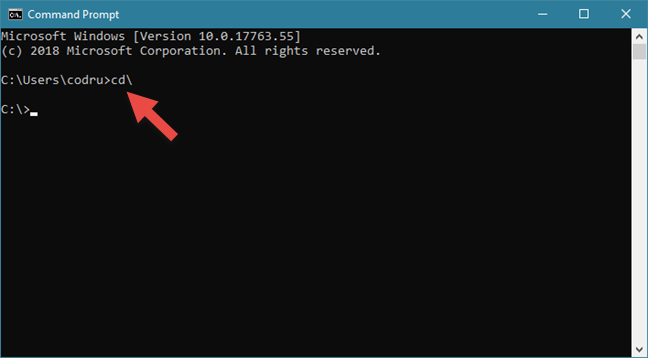
To change the working directory to another drive, execute command cd /D followed by a path to a directory. If a relative path is used, then the path should be relative to the CWD. Where the path should qualify the following criteria – To change the working directory, execute command cd followed by an absolute or relative path of the directory you are wanting to become the CWD. We can change the Current Working Directory to different paths in the system. Throughout the article, we will be using C:\Users as our CWD. To display the Current Working Directory, execute the cd command without any arguments.Īpparent from the above output, it is not necessary for us to print the cwd as it is already being displayed by the prompt. But for the sake of completeness, we would be describing it as well. This is because the default prompt in cmd displays the Current drive and path (CWD) along with the greater than sign ( > ) at all times ($P$G code).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
